Businesses face increasing pressure to adopt advanced blockchain solutions to enhance operational efficiency and mitigate risks. Traditional transaction sequencing methods often fail to meet the speed, security, and compliance demands. According to Capital One Shopping, 49% of global online purchases in 2022 were made using digital wallets. These numbers show the growing reliance on innovative financial technologies.
Shared Sequencing, Based Sequencing, and Smart Wallets offer innovative ways to address current challenges. These technologies are indispensable for forward-thinking FinTech companies. We have developed a non-custodial Dollet wallet and know all the intricacies of this topic.
Our article delves into the functionalities and strategic applications of these top blockchain solutions in FinTech based on our experience. We will explore how these technologies can empower businesses to streamline operations, mitigate risks, and stay ahead in the competitive fintech market.
Overview of Shared Sequencing
Shared Sequencing is a blockchain technology that optimizes transaction processing by distributing the Sequencing of transactions across multiple nodes. This decentralized approach enhances financial transactions’ efficiency, security, and speed.
The idea of shared Sequencing arose with rollups, which are Layer 2 scaling solutions for Ethereum and other smart contract platforms. Rollups enhance blockchain scalability and throughput by processing transactions off-chain. They gather multiple off-chain transactions into a bundle and record only the net state update on-chain.
Rollups achieve this in two main ways:
- Optimistic Rollups. These assume transactions in a bundle are correct unless proven otherwise. Transactions are finalized once a challenge period passes.
- ZK-Rollups. These use zero-knowledge proofs to verify the correctness of a transaction bundle’s state update. Transactions are finalized once the bundle is recorded on the blockchain.
In both methods, transactions occur off-chain and are bundled into smaller on-chain transactions. A sequencer’s role in a rollup is to organize these transactions into a bundle and generate the proof or state update for the bundle before handing it off to the proposer, who generates the new state root.
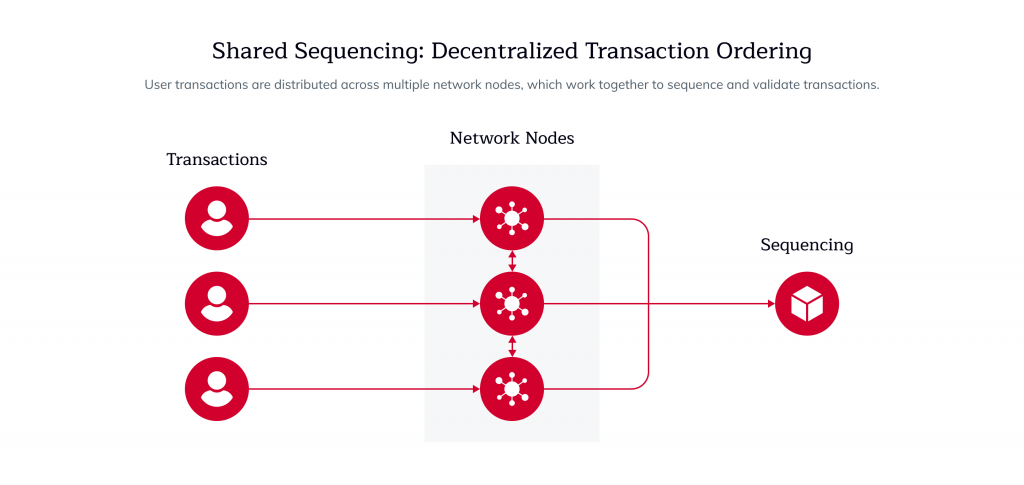
Top 3 Advantages of Shared Sequencing
Here are three main advantages of shared Sequencing.
Greater Efficiency
Decentralized sequencers allow blockchain networks to scale effectively by distributing transaction loads. As transaction volumes increase, this technology ensures the system can handle the demand without compromising performance. For FinTech companies, this means they can support more users and transactions without experiencing slowdowns.
Improved Security
Shared Sequencing enhances security by decentralizing the sequencing process. It makes it more difficult for malicious actors to manipulate transaction orders or execute attacks. This decentralized approach ensures that transactions are verified and processed securely. They maintain the integrity of the financial system.
Real-Time Processing
One of the standout advantages of shared Sequencing is its ability to enable real-time processing. By distributing transaction sequencing, this technology reduces latency, allowing for faster transaction confirmations. Real-time processing can significantly improve user experience and operational efficiency in the fintech industry, where speed is crucial.
Based Sequencing
Based rollup aims to leverage the benefits of Layer 1 sequencing to overcome some limitations of standard rollup designs.
In the model used by based rollups, Layer 1 block proposers take on sequencing responsibilities for the rollup. Collaborating with Layer 1 searchers and block builders, the proposer can include the next rollup block in the upcoming Layer 1 block.
Cost-Effectiveness
Based Sequencing is designed to be cost-effective by reducing the need for extensive computational power. Batching transactions minimizes resource consumption, resulting in lower operational costs. This approach also decreases the overall energy consumption and computational load, making it a sustainable and affordable solution for fintech companies.
Improved Throughput
The primary benefit of Based Sequencing is its ability to significantly increase transaction throughput. By processing multiple transactions at once, the system can handle a higher volume of transactions per second without compromising network security. This improved capacity is crucial for fintech businesses that must manage large transaction volumes efficiently.
Reduced Transaction Fees
By optimizing transaction processing, Based Sequencing reduces the complexity and resources needed, leading to lower transaction fees. This efficiency allows FinTech companies to offer more competitive pricing to their customers. Lower transaction fees enhance user satisfaction and attract more users to the platform.
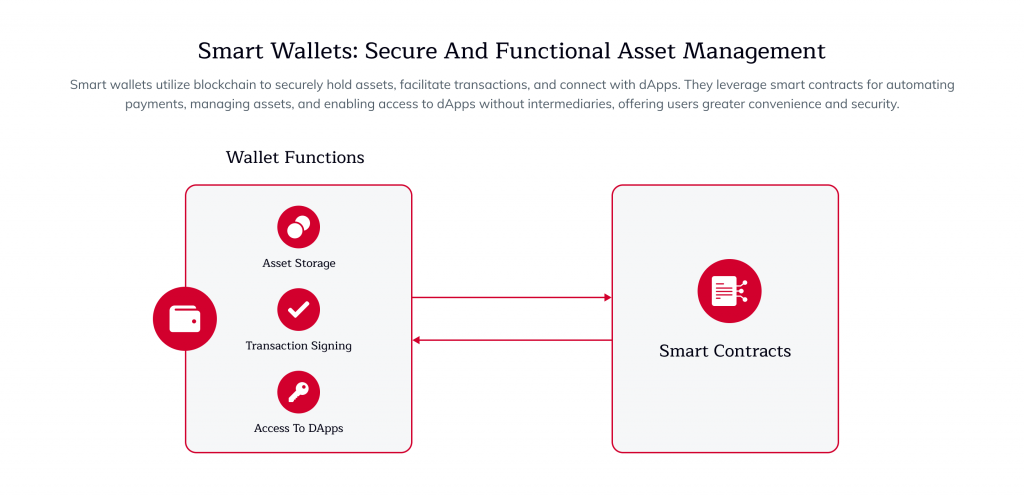
Exploring Smart Wallets
Smart Wallets are digital wallets equipped with advanced features like automation through smart contracts, integration with Ethereum dApps, and enhanced security measures. These wallets transform digital finance by providing users with more secure, efficient, and versatile financial management tools. With our expert cryptocurrency wallet development services, you can build smart wallets that support sequencing models, multi-signature security, and seamless dApp connectivity tailored to FinTech and Web3 use cases.
Automation
Smart wallets utilize smart contracts to enable seamless and secure automated transactions. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They allow for automatic and trustless transactions. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries, decreases transaction times, and minimizes the risk of human error, making financial transactions more efficient and reliable.
Integration with dApps
Smart Wallets facilitate easy access to decentralized applications (dApps) within the blockchain ecosystem. This integration allows users to interact with various dApps directly from their wallets, whether for finance, gaming, social media, or other purposes. By providing a unified platform for accessing dApps, Smart Wallets enhance user convenience and promote broader adoption of blockchain technology.
Enhanced Security Measures
Security is a critical feature of smart wallets. They utilize advanced encryption and authentication methods to protect user funds and data. These measures include:
- Multi-signature support
- Biometric authentication
- Hardware wallet integration
Users’ assets must be safe from unauthorized access and cyber threats in any DeFi wallet.
Conclusion
Shared Sequencing, Based Sequencing, and Smart Wallets offer transformative benefits for the fintech industry. These blockchain solutions address critical challenges and provide strategic advantages that significantly enhance operational efficiency and security. Key points:
- Shared Sequencing increases scalability, improves security, and enables real-time processing capabilities. It is particularly effective in cross-border payments, digital wallet transactions, and fraud prevention.
- Based Sequencing boosts transaction throughput, lowers operational costs, and reduces transaction fees. This solution benefits payment processing systems, blockchain-based supply chain management, and DeFi platforms.
- Smart wallets enhance user experience through automation, facilitate easy access to dApps, and offer advanced security measures. They are essential for non-custodial wallets, automated payment systems, and integration with DeFi platforms.
For FinTech companies looking to implement these cutting-edge blockchain solutions, partnering with an expert like IdeaSoft can be invaluable. Our proven track record in developing advanced blockchain solutions (case) ensures that you can effectively leverage Shared Sequencing, Based Sequencing, and Smart Wallets tailored to your specific needs.
Contact us for a consultation on how these innovative blockchain solutions can be implemented to transform your business operations and stay ahead in the competitive fintech market.

