If you follow the news of the crypto world, you’ve probably already heard about NFTs, which along with DeFi have become the hottest topics of 2020. Having gone from gaming to a promising way of real-world asset tokenization, NFTs have every chance of becoming a widespread solution, experts say. Read this article to find out what non-fungible tokens are, a new market disruptor, or just another hype.
Table of Contents:
- What is a non-fungible token (NFT)?
- How do non-fungible tokens work?
- NFT use cases
- The future of NFTs
- Summing up
What is a non-fungible token (NFT)?
Non-fungible tokens were first introduced back in 2017. Unlike regular cryptographic tokens, NFT represents a unique digital asset that cannot be replicated. Any cryptocurrency is essentially a token, be it Bitcoin or Ether or something else. These tokens are fungible because they are tradable for each other, and their value remains constant. Hence, you can easily exchange one Bitcoin for another Bitcoin. But this doesn’t work with non-fungible tokens, which display the rights to a unique asset of its kind. Essentially, NFT is a way of asset tokenization.
For example, you can digitize the right to a work of art and receive a token to prove it. There is only one such token that relates to your asset and you cannot find the same equivalent to it. Even if you exchange your token for an art object for another token that represents an art object, they are not the same or equal. Just like any real-world assets are unique, NFTs representing them are unique too.
Non-fungible tokens have a number of specific characteristics, which include:
- Uniqueness. Each NFT token contains a unique set of data and represents a unique asset.
- Indivisibility. You cannot divide NFTs into smaller denominations, unlike fungible tokens like Bitcoin, for example.
- Authenticity. Since NFT is powered by blockchain, it is quite easy to track the validity of your token and its owner thanks to such blockchain properties as traceability and immutability.
- Non-interoperability. NFTs cannot be directly traded one to another even if they are on the same platform. You can buy and sell NFTs on special marketplaces.
| Criterion | Fungible token | Non-fungible token |
| Type of token | Uniform | Unique |
| Exchangeability | Can be exchanged for a token of the same type | Cannot be exchanged for a non-fungible token of the same type |
| Divisibility | Divisible into smaller units(1$=100 cents) | Cannot be divided |
| Data registered in blockchain | Only the balance | ID, ownership, metadata |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Ethereum | Art, property (house) |
The main advantage of NFTs is their uniqueness, which allows us to apply them to any object in the real world, without the risk of fraud. As we remember, all data recorded on a blockchain remains there. Also, for many NFTs are an opportunity to trade real-world assets on digital exchanges.
How do non-fungible tokens work?
Currently, most NFTs are built on Ethereum using ERC-721 and ERC-1155 standards. The ERC-1155 token standard allows one contract to contain both fungible and non-fungible tokens. Software developers can use Ethereum’s off-the-shelf tools to create new NFTs. Meanwhile, other decentralized platforms like EOS and NEO also offer their NFT standards. Businesses looking to enter the NFT space can take advantage of professional NFT development services to build custom solutions tailored to their needs.
NFTs are implemented using smart contracts. Each token contains a set of unique information (metadata) recorded in its smart contract, and a blockchain guarantees the immutability of this data. The transfer of ownership of the NFT takes place using a blockchain transaction, which can only be authorized by the private key of the owner of the NFT, just like a regular blockchain transaction. Thus, we receive a reliable permanent digital confirmation of the ownership of the asset.
It is important to understand that the value of each token is unique. NFTs can be traded on open marketplaces that connect buyers to sellers. Examples of such NFT marketplaces are OpenSea, Rarible, Decentraland, and others.
Read The Ultimate Guide to Developing an NFT Marketplace
NFT use cases
The beginning of the use of NFT is associated with gaming. Games like CryptoKitties and Blockchain Cuties have allowed users to create rare items, and monetize them. In the game Gods Unchained, users can collect and sell unique cards. In these examples, blockchain looks like an interesting tool for maintaining the online economy of virtual worlds, but gradually this model began to be applied in the real world. Non-fungible tokens are great for real asset tokenization. Tokenization helps to increase the liquidity of assets in areas such as real estate, art, collectibles, and others.
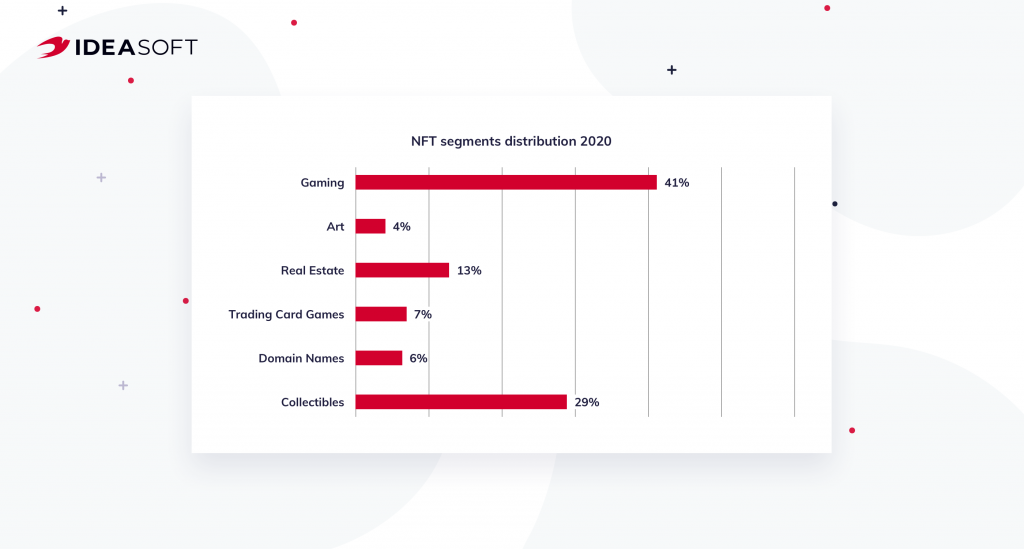
Here are some NFT use cases besides collectibles and gaming:
- Art – NFTs have opened up new opportunities for the art market. Tokens allow transferring the right to an object of art in a digital form, which makes it possible to earn money on the use of these objects in digital space. Blockchain allows you to track who exactly owns an art object and protect the rights of the author. You can already find platforms for publishing digital art such as OpenSea, Rarible, etc.
- Identity – NFTs can also be used for digital identity as they allow for the unique characteristics of each token. With the help of non-fungible tokens, we can digitize our academic qualifications, medical history, and other unique information. This will give users complete control over the use of their data.
- Domain names – NFT is an effective tool for decentralized domain name services. Tokens can now verify ownership of a specific crypto domain, such as name.eth or token.crypto.
The growing interest in NFT is driving new use cases for these tokens. The combination of NFT and DeFi is considered particularly advantageous, as reliable proof of ownership of a unique asset can make decentralized financial products even more popular.
The future of NFTs
The NFT market has shown growth in the past year. In the first half of 2020, the cumulative turnover of non-fungible tokens reached $232.5 million, showing an increase of 294.29%, compared to the first half of 2019, according to the Nonfungible.com report. The growing interest in non-fungible tokens is attracting new investments. According to the L’Atelier BNP Paribas report, NFT investments rose 299% in 2020. Also, Nonfungeable.com found that the number of buyers of NFT rose 66% in 2020. According to forecasts this year, we can also expect an increase in the NFT market as an interest in this technology has just begun to grow. NFT has yet to be proven to be effective or useless. Therefore, for now, we can expect the emergence of new projects related to non-fungible tokens.
Summing up
Non-fungible tokens differ from ordinary crypto tokens. They have such properties as uniqueness, indivisibility, and non-interoperability. Because of these properties, NFTs are an excellent way to tokenize real-world assets for further use in the digital space. It’s hard to say right now if NFT will be the next big thing in crypto, as interest in this topic is growing and we don’t have enough case studies to evaluate its effectiveness. However, the current projects look pretty promising, and there is no reason not to try new software solutions using NFT. ERC 404 tokens offer a new standard for managing unique digital assets.
If you have an idea for a blockchain project, the IdeaSoft team will be happy to help you bring it to life. More than 5 years of experience and 250+ completed projects have allowed IdeaSoft developers to gain extensive expertise. We worked with a variety of blockchain-based projects from creating smart contracts to building crypto exchanges. Check out the blockchain development services page and feel free to contact us to discuss your project.

