Discussions on scaling cryptocurrencies are ongoing, and several potential solutions to this issue have been in development for some time. The concept of private shards has gotten wider appliance in the last year. Now, it allows us to realize many technological solutions that previously were not available.
At IdeaSoft, we worked extensively in the blockchain domain. Our case studies demonstrate our vast expertise in a variety of industries. This is why we aim to shed light on private shards in public blockchain. This is a fairly new, young technology, but very promising. It will help a lot if you apply it correctly. This article will discuss the pros and cons of sharding blockchain as well as sharding in blockchain examples.
Should you use sharding technology for your solution?
Sharding is an excellent solution for solving scalability issues arising from growing transactions. The sharding approach enhances resource efficiency, enables customization for specific use cases, and is particularly advantageous in networks experiencing rapid expansion. Reach out to our team of blockchain experts and we will help you to define the best solution for your project!
Table of Contents:
- Understanding Sharding in Blockchain
- Sharding Work Principle
- What problems can be solved with sharding?
- Private Shards: Concept and Purpose
- Technical Implementation of Private Shards
- Real-World Examples
- Summary
Understanding Sharding in Blockchain
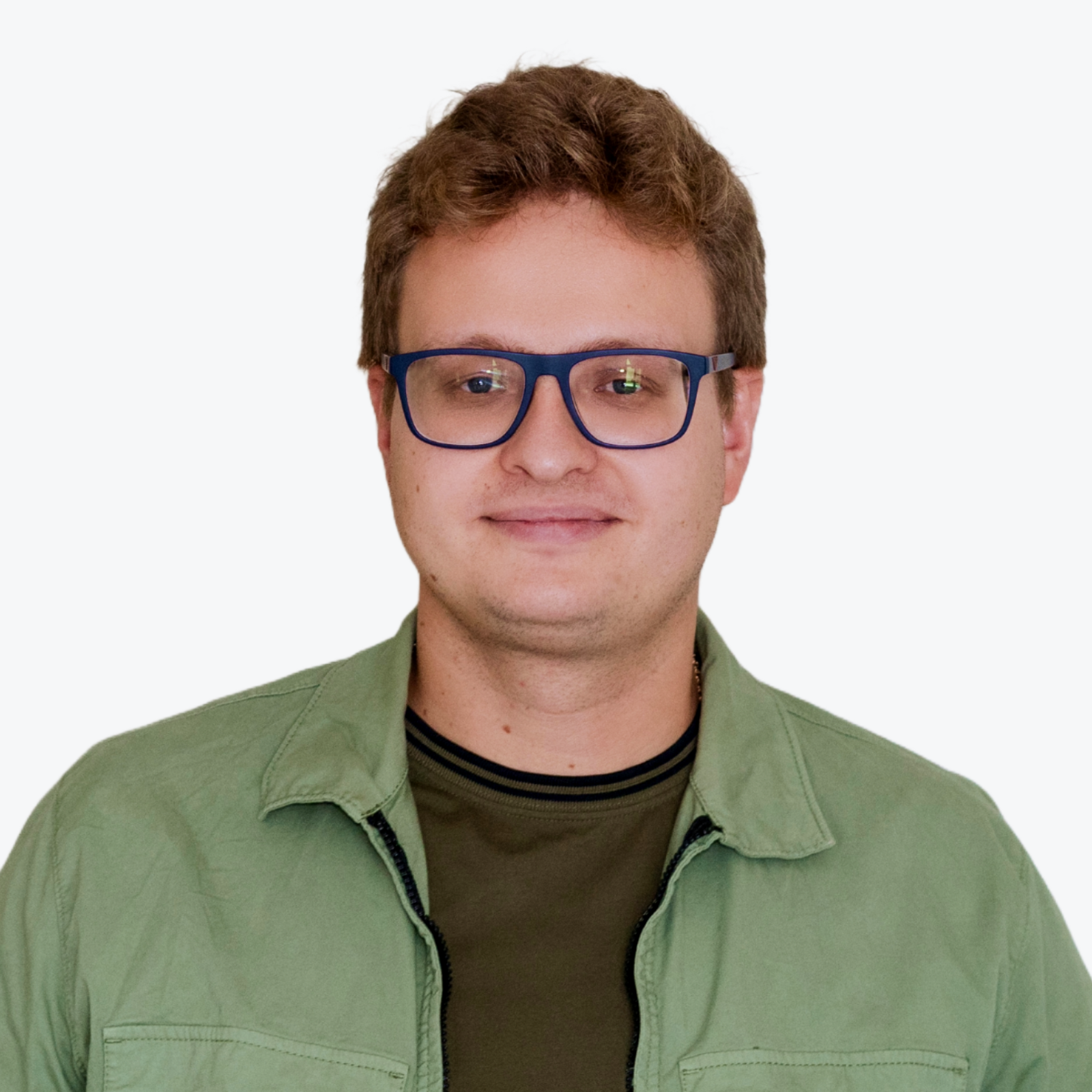
The definition of sharding blockchain is complex. Sharding is a method that allows you to separate and provide storage for a specific set of information. With the help of sharding technology, it is possible to create a database where nodes will be placed. They are formed into individual servers. According to blockchain sharding technology, separate networks are divided into separate individual clusters.
A node is assigned for each cluster. It simplifies the set of operations and transactions. Through the servers, users make financial transfers. With large loads, failures can occur, so optimal solutions are required to solve such a problem.
If you distribute the blockchain in separate segments, the system will be able to work much faster. You can get rid of excessive workloads and likely failures. The speed of transactions will increase several times. Blockchain sharding technology has proven itself in practice. It is already used in:
- Ethereum
- Zilliqa
- Polygon
- Avalanche
- NEAR
So, if you have your own blockchain project and want to move it to the next level, a great idea is to consider blockchain sharding technology.
Sharding Work Principle
You can understand the principle of sharding in the example of Ethereum. This blockchain includes a huge number of nodes or individual computers. They all use a certain percentage of the total hash rate responsible for the blockchain`s functionality. DApps are also managed using a hash rate.
Ethereum was based on the concept of sequential execution. All nodes had to be responsible for individual transactions and process them. Transactions went through a verification process that took much time. Statistics showed that Ethereum conducted at least 20 transactions every second. But if compared with other systems, such as Visa, the throughput here is at least 20,000 transactions for a similar time.
If developers added computers to the network, this solution would not increase the whole system’s efficiency. The register is stored on separate devices. Computers would only increase the verification sequence.
Instead of adding new computers to the network, the Ethereum team has implemented sharding technology. This way, they improved the process of each individual transaction. Ethereum is now divided into shards with many registries. Nodes only manage certain registry classes to which they are attached. Their task includes the execution of all processes and transaction confirmation. Sharding makes Ethereum and Binance for DEX more scalable and efficient, meeting the growing demands of decentralized exchanges.
What problems can be solved with sharding?
If there is a scaling problem, the sharding concept can be utilized to implement the blockchain of the future. When blockchain is gaining popularity and demand among users, they use all available tools and perform various financial transactions. As a result of this, the load level increases. The network is also loaded due to running applications, if any.
At the maximum load, the speed of financial transactions decreases. The blockchain cannot be extended, and future changes and improved capabilities cannot be implemented. When transaction activity increases, nodes will need to be improved so that they can verify more transactions. Sharding can solve the scaling problem, so it is worth considering this option.
Private Shards: Concept and Purpose
Private shards are defined by their unique set of characteristics that distinguish them in the blockchain ecosystem:
- Selective visibility. Private shards allow for selective visibility, ensuring only authorized participants can access and view specific transaction data. This enables a level of confidentiality vital for sensitive business operations.
- Permissioned access. Access to private shards is permissioned, meaning only designated entities possess the keys to unlock and participate in the transactions within that shard. This controlled access ensures a secure and trusted environment.
- Scalability and performance. Private shards contribute to the overall scalability of a blockchain network by distributing the load across multiple shards. This results in enhanced performance, reducing congestion and transaction times compared to traditional public blockchains.
- Smart contract functionality. Private shards integrate smart contract functionality. This allows for the execution of complex, automated business processes within the private and secure confines of the shard.
The advantages of private shards in blockchain become particularly evident when examining their use cases:
- Enterprise blockchain solutions. private shards are tailor-made for enterprise-level blockchain applications, where data privacy and confidentiality are paramount. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management can benefit significantly from private shards’ secure and scalable nature.
- Sensitive data transactions. When dealing with transactions involving sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII) or proprietary business processes, private shards offer a secure enclave for these exchanges. This is critical for compliance with data protection regulations.
- Consortium blockchains. In consortium blockchains where a limited number of trusted parties are involved, private shards provide an ideal solution. They maintain transparency among consortium members while safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Private shards also serve as a robust solution to the limitations inherent in public blockchains like privacy concerns, scalability bottlenecks, and regulatory compliance.
Technical Implementation of Private Shards
Let’s revise the concept of private shards on the solution from our long-lasting partner, NEAR blockchain. Private shards within the NEAR network introduce seamless interoperability where public chain contracts can engage with private shard contracts and vice versa.
This interaction is facilitated through the existing mechanism managing cross-shard routing, offering a transparent experience for both users and developers without necessitating additional efforts. Remarkably, public contracts can interact with private ones without explicit knowledge of the underlying private nature.
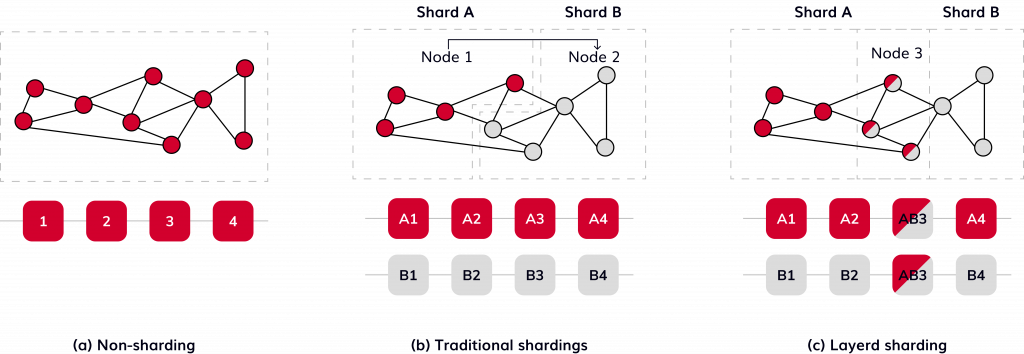
Consider the scenario where two private shards seek to interact directly, bypassing public shards. The solution lies in the establishment of a shared identity space. Each private shard is endowed with a unique name akin to web domains. For instance, the University of Berkeley and Tencent might possess accounts named “berkeley.edu” and “tencent.com,” respectively.
Within their private shards, specific applications are allocated sub-accounts. Using the example of a real estate ownership tracking application, these could be “properties.berkeley.edu” and “properties.tencent.edu.” In the case of a property transaction between these entities, a cross-private shard transaction occurs. It is followed by public chain settlement if the information needs validation by the public.
Want to build your solution based on the private shards concept?
Let us help you figure everything out, and correctly draw up the requirements for your project
Real-World Examples
Today, many platforms implement sharding blockchain to reduce server load. As a result, they were able to increase the interest of users.
A striking example is the Zilliqa platform. Specialists at the testing stage were able to achieve an excellent result. They increased the number of transactions to 2800 per second.
As we described above, the NEAR blockchain also applies sharding technology. Developers can create and use various applications with the help of the offered tools. Meanwhile, nodes can freely function on devices that do not have a high level of performance.
One of the greatest applications for private sharding technology is the ability to implement a digital ID system based on blockchain that will be secure and transparent from one perspective yet accessible by a certain amount of people interested in a particular location from the other. Polygon and Avalanche Subnet are pioneers in this direction, providing unique privileges for realizing digital identity.
Moreover, the application of digital ID developed on blockchain reveals a rich set of benefits and opportunities. It is not only a new stage in the evolution of private corporations but also of healthcare services. It creates prospects for a more secure, efficient, and sustainable digital environment. These technologies can be successfully deployed in various fields, such as large corporations, medicine, and many others.
For example, large corporations need a digitized identity on blockchain due to its tamper-resistant records and advanced encryption. This way, large corporations can reduce the risk of identity theft and fraud. Blockchain’s efficiency in identity verification can significantly cut costs and enhance user control. This is due to streamlined processes and automated consent management via smart contracts. The decentralized nature also adds resilience by eliminating single points of failure, fostering trust among participants, and offering corporations scalable solutions through Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) providers.
Read also: Use Cases of Shared & Based Sequencing
By the way, there’s a trend toward private solutions for the next year. Fortune Business Insights says the private blockchain sector is poised to command a substantial revenue share throughout the coming years.
Private solutions and services empower organizations to adopt regulations with reduced transaction costs, facilitating transaction reversals. The heightened scalability of private digital ledger solutions is anticipated to drive demand significantly.
Adaptation of private solutions helps speed up transactions and lower costs while making solutions scalable. We expect a great growth in demand for private blockchain technology specialists. Besides, consortium and hybrid models expect great adoption for the federal layer solutions.
Fortune Business Insights Complex Market Research 2024
Summary
Today, the whole blockchain industry is trying to forge a connection between the internet and blockchains that are poised to drive the future. A pivotal initiative contributing to this mission is private shards. Private shards serve as a foundational element, contributing to establishing an ecosystem wherein businesses, users, and partners can seamlessly interact. By offering advanced blockchain development solutions, we help businesses unlock new opportunities and create secure, scalable ecosystems tailored to their needs.
We at IdeaSoft contribute to the evolution of a digital landscape by addressing current challenges and paving the way for the transformative potential of blockchain technologies. If you want to build private shards or develop blockchain applications, feel free to contact us!

